ADAS Definition
ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. ADAS refers to a set of safety features and technologies in modern vehicles that assist the driver in driving and help to avoid accidents. These systems use various sensors, cameras, and other technologies to gather information about the vehicle’s surroundings, and then provide the driver with visual, audible, or haptic warnings or even take control of the vehicle to prevent or mitigate a collision. Some common examples of ADAS features include automatic emergency braking, lane centering, adaptive cruise control, blind-spot detection, and parking assistance. The ultimate goal of ADAS is to make driving safer, easier, and more efficient.
How does ADAS Work?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) use sensors like cameras, radar, and more to keep an eye on the road and your vehicle’s surroundings. These sensors send information to a smart computer in the car, which uses software to understand what’s happening around you. The computer can warn the driver about potential dangers, like getting too close to another car or drifting out of the lane. In some cases, ADAS can even help the car take actions, like applying the brakes if a collision is about to happen or steer your vehicle in the lane. It’s like having a helpful co-pilot that makes driving safer and more comfortable.
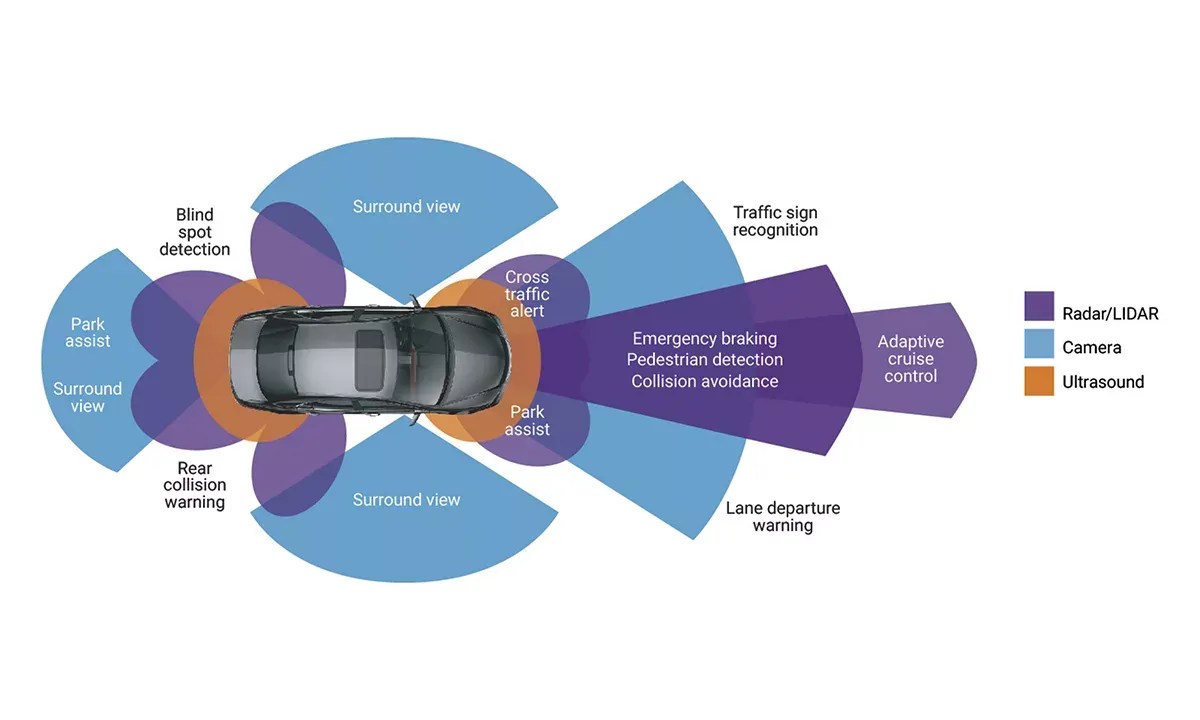
What are some ADAS applications?
Below are the most common ADAS applications found in modern vehicles:
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Adaptive cruise control, or ACC, automatically adjusts your vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the car ahead. It can slow down, speed up or stop your vehicle based on traffic conditions. ACC is particularly useful on the highway or in stop and go traffic.
Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA)
Lane Departure Warning, or LDW, alerts you if your vehicle starts drifting out of its lane without using the turn signal. Lane Keeping Assist, or LKA, can gently steer your vehicle back into the lane if you’re unintentionally drifting.
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
Automatic Emergency Braking, or AEB can detect if a collision with the vehicle ahead is imminent and automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact.
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM)
Blind Spot Monitoring, or BSM alerts you if there’s a vehicle in your blind spot, helping you avoid potentially dangerous lane changes.
Parking Assistance
Parking Assistance features can help with parallel parking or perpendicular parking by providing guidance and controlling speed and/or steering inputs.
Cross Traffic Alert
Cross Traffic Alert alerts you when maneuvering in or out of a parking space, this feature warns you if there’s traffic coming from the sides.
Traffic Jam Assist
Traffic Jam Assist can help you navigate through slow-moving traffic by automatically controlling acceleration, braking, and steering within certain limits.
Driver Drowsiness Detection
This feature can monitor your driving behavior and alert you if it detects signs of drowsiness or inattentiveness.
Adaptive Headlights
These headlights automatically adjust their intensity and direction based on steering angle and driving conditions, enhancing visibility at night.
These are just a few examples of the many ADAS applications available. The goal of these technologies is to enhance driver safety, reduce the likelihood of accidents, and make driving more comfortable and enjoyable. However, it’s important to stay informed about the specific capabilities of your vehicle’s ADAS and understand their limitations.
What is the future of ADAS?
The future of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with vehicles and navigate our roads. As technology continues to advance, ADAS will evolve from its current role as a co-pilot to become a more integrated and capable driving partner. We can expect to witness the gradual emergence of higher levels of automation, enabling vehicles to take on more complex driving tasks independently, especially on highways and in controlled environments. This will not only enhance safety by reducing human error but also provide drivers with newfound freedom to engage in other activities while on the road.
Furthermore, the fusion of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and increasingly sophisticated sensors will enable ADAS to interpret and respond to the driving environment with unprecedented accuracy. These systems will become more adaptable and predictive, learning from individual driving patterns and real-time road conditions to optimize their assistance. Vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication will also become integral, allowing vehicles to share information and coordinate actions, leading to smoother traffic flow and enhanced safety. Ultimately, the future of ADAS holds the promise of safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experiences while paving the way for the eventual transition to fully autonomous vehicles.
What are the levels ADAS?
The levels of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in the J3016 standard. These levels describe the extent to which a vehicle’s automation can handle driving tasks, ranging from no automation (Level 0) to full automation (Level 5). Here are the different levels of ADAS:
Level 0 – No Automation: The driver is responsible for all aspects of driving. There are no automated systems in place, aside from basic warnings or momentary assistance.
Level 1 – Driver Assistance: This level involves systems that can assist with either steering or acceleration/deceleration, but not both simultaneously. For instance, adaptive cruise control (ACC) is an example of Level 1 automation.
Level 2 – Partial Automation: Level 2 vehicles have the capability to control both steering and acceleration/deceleration simultaneously. However, the driver must remain engaged and ready to take over at any moment. Tesla’s Autopilot is an example of Level 2 automation.
Level 3 – Conditional Automation: At this level, the vehicle can manage most aspects of driving in certain conditions. The driver can disengage from active control, but they must be prepared to intervene when prompted by the system. Level 3 automation is more prevalent in controlled environments like highways.
Level 4 – High Automation: Level 4 vehicles can perform most driving tasks and functions autonomously within specific conditions or environments, without requiring human intervention. However, the vehicle’s autonomy is limited to certain scenarios, and the driver might need to take over in exceptional situations.
Level 5 – Full Automation: At this highest level of automation, the vehicle is fully capable of performing all driving tasks in any environment and under any conditions. There’s no need for a human driver to be present, and the vehicle operates autonomously without any human intervention.

It’s important to note that even at higher levels of automation, current regulations and safety considerations mean that a certain level of human supervision or intervention might still be required in certain situations. The development and deployment of ADAS at these levels are ongoing processes.
How can drivers benefit from ADAS?
Drivers can benefit from ADAS features in many ways. Some of the key benefits include
Increased safety – ADAS features can help drivers avoid accidents by providing warnings about potential hazards and even taking control of the vehicle to prevent a collision.
Reduced driver fatigue – ADAS features such as adaptive cruise control and lane centering can help reduce the stress and fatigue associated with driving, especially on long trips and traffic jams.
Improved convenience – ADAS features such as parking assistance and traffic sign recognition can make driving more convenient by reducing the need for the driver to perform certain tasks manually.
Better fuel economy – ADAS features such as eco-driving assistance can help drivers use fuel more efficiently, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Enhanced driving experience – ADAS features such as adaptive headlights and intelligent speed adaptation can enhance the driving experience by improving visibility and comfort.
Overall, ADAS features can help drivers stay safer, more comfortable, and more efficient on the road. Contact us today to schedule a DAVCO Drive to experience your vehicle’s ADAS features!

